In many ways BAM can be considered as a key enabler for achieving agility in the business processes across the enterprise. Agility is all about the sustenance to change. It’s the ability of a business to accommodate and respond to a change faster. BAM can address the key pre-requisites to achieve agility in the enterprise:
• Visibility into daily operations and faster response to variations from the normal trend
• Awareness of change both from external and internal sources
• End-to-end view of the processes with important signs, corrective and proactive measures to be taken by the stakeholders.
Figure 4.1 shows how the BAM solutions and the agility pre-requisites are mapped to the example stated in this article. It’s important to identify the key factors that can increase the agility of the business. For example, the business should focus on external sources that are applicable to the domain and identify the stakeholders who need to get notified on the change and also the people who can act effectively. The more quickly the respond state is reached, the more agility the business will gain.
Figure 4.1: BAM for Agility
Optimizing Business Processes
In a conventional technical way BAM does not have capabilities for performance modeling and application tuning which are the key features of performance engineering. But if BAM is considered from the business process point of view, it provides an approach on how to monitor, tune and track the business processes for performance improvement. This feature in turn adds up in achieving agility, responsiveness and resilience to the business. Eventually these are the vital ingredients needed to optimize the performance of a business process.
Solutions and Implementations
There are several distinct Business Activity Monitoring Solutions present today. Some of them are offered by vendors which are focused exclusively on the Business Activity Monitoring sector such as Systar. Most of the realistic Business Activity Monitoring applications in the market come from the primary enterprise software vendors such as Microsoft, IBM, TIBCO and Oracle. These companies were able to sense the future need of BAM in the marketplace and stapled Business Activity Monitoring capabilities with some of their existing software products. For example Microsoft introduced Business Activity Monitoring features to its BizTalk Server suite, IBM added them to WebSphere; and Oracle enhanced its application server offering with Business Activity Monitoring features. Some popular BAM solutions available today are briefly described below.
TIBCO BusinessFactor: TIBCO BusinessFactor™ software enables the development and delivery of performance visibility and business activity monitoring (BAM) solutions that let users quickly understand current operational performance in context of business objectives, past performance and related activities. It collects and correlates data from across the organization, presents information via customizable interactive dashboards, and alerts users when thresholds are exceeded. By performing these functions, the software helps users more quickly and accurately identify and address risks and opportunities.
It Visual representations of data – including maps, blueprints, technical drawings, charts, or graphs – give users the ability to analyze current conditions and performance for any level of location specificity or timeframe to quickly identify trends and predict likely outcomes. BusinessFactor's intuitive user interface shows critical performance indicators and supporting contextual information so users can perform quick historical analysis, drill into data, and take action. BusinessFactor also gives users the ability to collaborate with other users and interact with systems and processes to take appropriate action.
TIBCO SpotFire: By the way, nowadays TIBCO is promoting a more dynamic product in this area called SpotFire. SpotFire Operations Analytics is designed not only to monitor real-time business events but also to create and deliver root-cause analysis applications in response to those events automatically. Unlike reporting or dashboard based tools, those can only provide alerts on operational problems, SpotFire helps in solving problems, by automatically merging real-time monitored data with contextual information from multiple sources into applications designed to find outliers, trends and relationships.
Oracle Business Activity Monitoring: Oracle BAM is a key technology component of Oracle Fusion Middleware and SOA stack of products. It satisfies a rising need to enable Business Executives and particularly operations managers, to make decisions by making real-time actionable information available 24x7. Visibility into key business metrics empowers managers to improve the efficiency of their business processes in a step-by-step approach to process optimization.
Features of Oracle BAM
The proposed Business Activity Monitoring is Oracle BAM. By deploying the SOA framework and using BAM for monitoring the services, business users can derive actionable timely intelligence on their business operations by monitoring the flow of data, service requests, and process invocations. All the components of Oracle SOA Suite including Oracle BEPL Process Manager (Oracle BPEL PM) and/or the integration adaptors can be configured to sends Oracle BAM information emanating from the various integrated application processes using the JMS protocol. With Oracle BPEL PM this can be achieved by leveraging the built in “sensor” technology wherein a part or the entire state of an instance transaction at a process node can be sent to Oracle BAM as a JMS message for further analysis. Oracle BAM can then correlate disparate events that it received, as messages, within the context of pre-defined monitoring models and rules that can relate to business process KPIs to alert business users of process problems and opportunities.
Architecture Overview of Oracle BAM
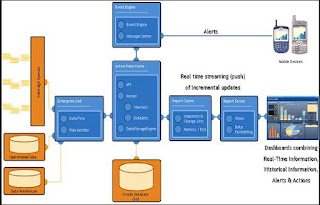
The Oracle BAM architecture utilizes messaging, data integration, advanced data caching, analytics monitoring, alerting, and reporting technology to deliver requested critical information within seconds of an event or change in status. Because the primary source of data is messages, Oracle BAM is able to update reports and generate alerts at speeds that traditional architectures simply can’t match. Oracle BAM can accept tens of thousands of updates per second into a memory-based persistent cache that is at the center of the Oracle BAM architecture. Any application can send events using Web services or over any JMSbased messaging protocols. Legacy application can integrate with Oracle BPEL PM using custom created adaptors and can in turn integrate with Oracle BAM via the Oracle BPEL PM native sensor architecture. Oracle BAM can additionally also send alerts to external web services when specified threshold conditions within the analytics engine are met. The figure 4.2 shows the Oracle BAM architecture.
Figure 4.2: Oracle BAM architecture
Business process data can be monitored and tracked using by Oracle Business Activity Monitor. Oracle Business Activity Monitoring (Oracle BAM) is a complete solution for building interactive, real-time dashboards and proactive alerts for monitoring business processes and services. Oracle BAM gives business executives and operation managers the information they need to make better business decisions and take corrective action if the business environment changes.
Figure 4.3: Oracle BAM and surrounding components
IBM WebSphere Business Monitor: IBM WebSphere Business Monitor (WBM) offers real-time insight into business processes.
WBM extends the extensive distributed platform for monitoring of events native to the mainframe platform. It provides business users with a real-time, end-to-end view of business process performance on user-friendly and customizable dashboards, corporate portals and mobile devices, as well as on the desktop. It can improve business results by enabling business users to preempt problems with predictive KPIs and to detect and manage business situations. It boosts up productivity by empowering business users to create new dashboards, KPIs and alerts with minimal IT involvement. It accelerates continuous process improvement and business innovation through a tight integration with other IBM BPM products.WebSphere Business Monitor V6.1 provides two types of dashboards: Web-based dashboards and portlet-based dashboards. Web-based dashboards are implemented as Web pages. Portlet-based dashboards are a component of WebSphere Business Monitor V6.1 that operates within the WebSphere Portal V6.0.1.1 environment. Figure 4.4 on and Figure 4.5 illustrate the runtime architecture respectively. As indicated by the flow in both figures, you follow this sequence:
1. After you finish the development of the monitor model, export the resulting monitor application that is deployed into the runtime environment (WebSphere Application Server, WebSphere Enterprise Service Bus, or WebSphere Process Server) by using the WebSphere Administrative Console. Ensure that you configure the WebSphere Business Monitor server application to link appropriately to CEI to be registered to consume events from the emitting application.
2. On another server (for example, WebSphere Process Server or WebSphere MQ Workflow), deploy the application that emits events to a CEI server.
3. Upon receipt of the registered event types, the CEI server sends the appropriate Common Base Event to the server registered in step 1.
4. The monitor model executes. It polls for events waiting on the queue, processes them according to the monitor model instructions, and stores business measures to the Monitor database.
Optionally, the monitor model application can obtain real-time event-related data from the event or data source through code that you can provide and invoke as a user-defined XPath function.
1. Optionally, in addition to receiving events as in step 3, the monitor model application can detect business situations (for example, thresholds) and emit events that can be consumed by the WebSphere Business Monitor action services.
2. The CEI server routes events received through the event or data source or the monitor model application to the action services.
3. The action services component takes action such as sending notifications, calling Web services, and invoking Service Component Architecture (SCA) components to perform actions.
Independently, the business user uses the dashboards, which invoke Representational State Transfer (REST) services to return data from the Monitor database and show monitoring results through different views.
Figure 4.4 shows usage of the lightweight Web dashboard, which is implemented as Web pages. DB2 Alphablox package installation is optional and is only the prerequisite for use of the dashboard’s dimensional and report views.
Figure 4.5
Figure 4.5 shows usage of the Portal dashboard, which uses WebSphere Portal Server to invoke a REST service. DB2 Alphablox package installation is optional and is only the prerequisite for use of the dashboard’s dimensional and report views.
Systar Business Activity Monitoring for Telecom: Systar Business Activity Monitoring (BAM) enables telecom firms to go beyond simply monitoring network and IT infrastructure processes, instead delivering a clear, 360-degree view of how incidents affect the health of critical business services that must seamlessly flow together.
Microsoft Business Activity Monitoring: Pro Business Activity Monitoring in BizTalk 2009 focuses on Microsoft's BAM tools, which provide a flexible infrastructure that captures data from Windows Communication Foundation, Windows Workflow Foundation, .NET applications, and BizTalk Server.
Microsoft BAM allows the user to manage aggregations, alerts, and profiles to monitor relevant business metrics (called Key Performance Indicators or KPIs). It provides an end-to-end visibility into the business processes, providing accurate information about the status and results of various operations, processes and transactions so the users can address problem areas and resolve issues within the business.




No comments:
Post a Comment